Introduction:
High Availability (HA) is a critical aspect of network design, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity and minimizing downtime. Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a key tool for achieving redundancy in network infrastructure. Configuring HSRP correctly is essential for seamless failover and robust network operations. This article delves into the intricacies of HSRP configuration, providing insights and best practices for network administrators.
Table of Contents
Understanding HSRP:
HSRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol designed to provide fault-tolerant default gateway redundancy. It allows for the establishment of a virtual IP address and a virtual MAC address shared among a group of routers, ensuring continuous availability of network resources even in the event of a router failure.
Key Components of HSRP:
- Active Router: The router in an HSRP group currently forwarding packets for the virtual IP address.
- Standby Router: A router in an HSRP group that is ready to become the active router if the current active router fails.
- Virtual IP Address: The IP address shared among routers in the HSRP group, serving as the default gateway for devices on the subnet.
- Virtual MAC Address: A MAC address associated with the virtual IP address, facilitating transparent failover at the data link layer.
HSRP Configuration Steps:
Configuring HSRP involves several steps, including interface configuration, HSRP group creation, and fine-tuning parameters for optimal redundancy.
Step 1: Interface Configuration
Begin by configuring the interfaces participating in HSRP. This includes assigning IP addresses and enabling HSRP on the interfaces.
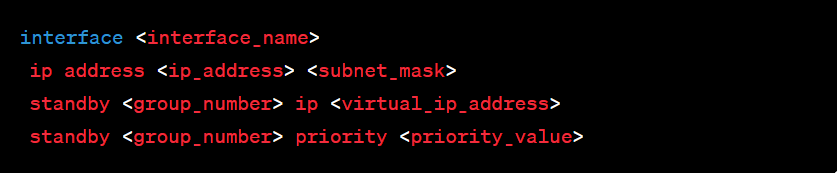
Step 2: HSRP Group Creation
Create HSRP groups on each interface, specifying the virtual IP address and other parameters such as priority and preempt options.
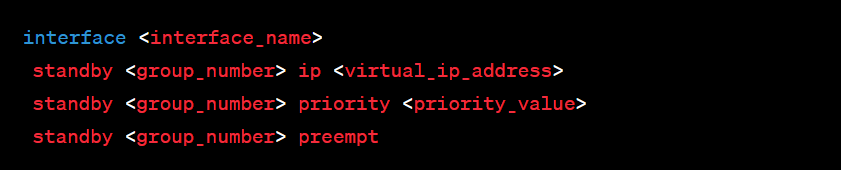
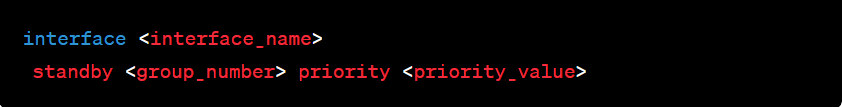
Step 3: Priority Configuration
Set priorities for routers within the HSRP group to determine the active router. Higher priority values indicate a higher likelihood of becoming the active router.
Step 4: Preemption Configuration
Configure preemption to allow routers with higher priorities to preempt routers with lower priorities and become the active router upon recovery.

Step 5: Verification
After configuring HSRP, verify the status and operation of the HSRP groups using commands such as show standby.

Best Practices for HSRP Configuration:
To ensure optimal performance and reliability, consider the following best practices when configuring HSRP:
- Symmetric Configuration: Ensure consistent HSRP configuration across all routers in the group, including virtual IP addresses, priorities, and timers.
- Priority Assignment: Assign priorities based on router capabilities and roles within the network hierarchy.
- Load Balancing: Implement load balancing by adjusting priorities or using HSRP tracking to distribute traffic across routers.
- Monitoring and Testing: Regularly monitor HSRP status and perform failover testing to verify proper operation and readiness.
- Security Considerations: Implement HSRP authentication to prevent unauthorized routers from participating in HSRP groups.
Conclusion:
HSRP configuration plays a crucial role in establishing redundant network infrastructure and ensuring high availability of network services. By following the outlined steps and best practices, network administrators can deploy HSRP effectively, mitigating the risk of downtime and providing seamless failover capabilities for critical network resources. With proper configuration and maintenance, HSRP remains a cornerstone of resilient network design in modern IT environments.
